基于FLOW90系列/R7S910001CFP主控芯片的中小功率书本式伺服系统解决方案
 481
481
 拍明
拍明
概述
随着目前智能设备和机器人的发展,伺服系统的应用也越来越广泛。我们对指标功能要求更加多样化,不同的应用对结构也有不同的需求。本文为迎合中小功率的书本式架构的伺服系统提供了高指标、结构紧凑、可提高设备散热能力的解决方案。
优势
• 中小功率书本式IGBT模块(FLOW90系列),使约1000-5000W功率的伺服系统的主板和散热器间成90度,呈书架式架构,易通风散热且小型化;
【FLOW90】
84 mm x 30.5 mm
Possible features
90° mounting angle between heatsink and PCB
Clip or screw-on heatsink mounting
Clip-in PCB mounting
Thermo-mechanical push-and-pull force relief
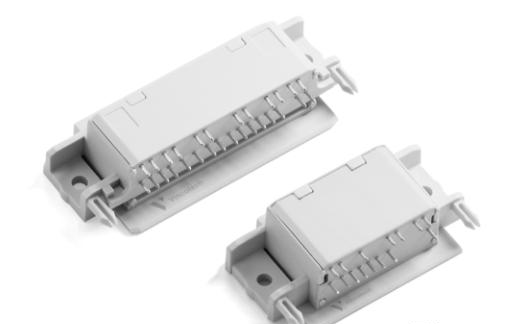
Vincotech 全新的创新型 flow90 sixpack 模块 - 书本式逆变器和机架式电源的完美匹配。
Vincotech 现已提供简单而智能的 flow90PACK 0 和 flow90PACK 1 模块,最大额定电流和电压可达 75A 和 1200V,可完美搭配书本式逆变器和机架式电源应用。很多此类应用要求散热片与PCB呈垂直安装,迫使工程师们只能使用特殊设计印制板或昂贵的L形散热片。现在,flow90 0 和 flow90 1 封装的 sixpack 模块可同时实现空间和成本的节约,彻底解决了这一问题。
特性:
模块符合DIN和IEC标准
易于定制的单元拓扑结构
按需提供预涂相变材料
可选的clip-in安装结构,有助于简化组装
可以和印制板上其他直插器件一起进行波峰焊
降低热机械应力和推拉力
有两种尺寸可供选择:
flow90 0 - 38 x 66 x 21 mm
flow90 1 - 35 x 84 x 21 mm
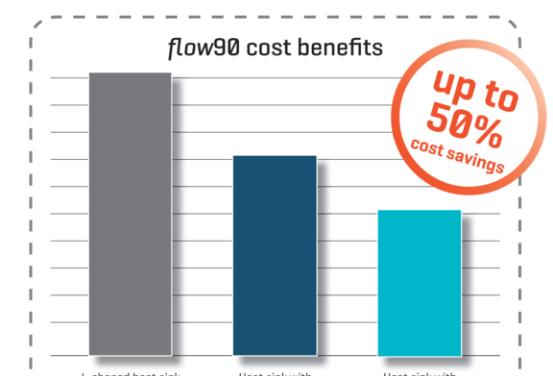
Main benefits
Eliminates the need for L-shaped heat sinks to slash costs
by as much as half
Compact housing enables 90° angle between heat sink and
PCB for up to 40% savings
Installs on the same PCB side as other through-hole components
Optional clip-in PCB mounting helps simplify assembly
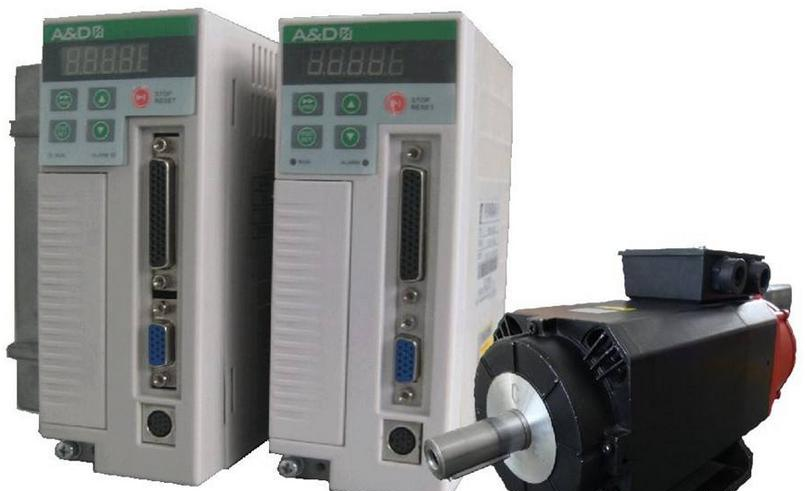
• 具有R4F内核的32位MCU(R7S910001CFP),最高600MHz主频,内部集成工业以太网Ether CAT控制器、编码器接口(可支持多种协议的编码器)、单相和三相伺服逆变控制功能。
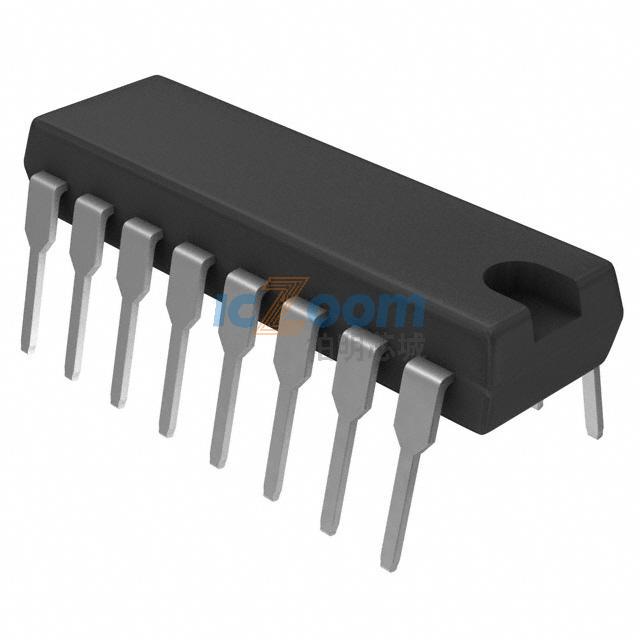
【R7S910001CFP】
300 MHz/450 MHz/600 MHz, MCU with ARM Cortex®-R4 and -M3*1, on-chip FPU, 498/747/996 DMIPS, up to 1 Mbyte of on-chip extended SRAM, Ethernet MAC, EtherCAT*1, USB 2.0 high-speed, CAN, various communications interfaces such as an SPI multi-I/O bus controller, ΔΣ interface, safety functions, encoder interfaces*1, and security functions*1

Features
■ On-chip 32-bit ARM Cortex-R4 processor
• High-speed realtime control with maximum operating frequency of 300/450/600 MHz Capable of 498/747/996 DMIPS (in operation at 300/450/600MHz)
• On-chip 32-bit ARM Cortex-R4 (revision r1p4)
• Tightly coupled memory (TCM) with ECC: 512 Kbytes/32 Kbytes
• Instruction cache/data cache with ECC: 8 Kbytes per cache • High-speed interrupt
• The FPU supports addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, multiply-and-accumulate, and square-root operations at singleprecision and double-precision.
• Harvard architecture with 8-stage pipeline
• Supports the memory protection unit (MPU)
• ARM CoreSight architecture, includes support for debugging through JTAG and SWD interfaces
■ On-chip 32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 processor
(in products incorporating an R-IN engine)
• 150-MHz operating frequency • On-chip 32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 (revision r2p1) • RISC Harvard architecture with 3-stage pipeline • Supports the memory protection unit (MPU)
■ Low power consumption
• Standby mode, sleep mode, and module stop function
■ On-chip extended SRAM
• Up to 1 Mbyte of the on-chip extended SRAM with ECC
• 150 MHz
■ Data transfer
• DMAC: 16 channels × 2 units
• DMAC for the Ethernet controller: 1 channel
■ Event link controller
• Module operations can be started by event signals rather than by
interrupt handlers.
• Linked operation of modules is available even while the CPU is in
the sleep state.
■ Reset and power supply voltage control
• Four reset sources including a pin reset
• Dual power-voltage configuration: 3.3 V (I/O unit), 1.2 V(internal)
■ Clock functions
• External clock/oscillator input frequency: 25 MHz
• CPU clock frequency: Up to 300/450/600 MHz
• Low-speed on-chip oscillator (LOCO): 240 kHz
■ Independent watchdog timer
• Operated by a clock signal obtained by frequency-dividing the clock signal from the low-speed on-chip oscillator: Up to 120 kHz
■ Safety functions
• Register write protection, input clock oscillation stop detection,CRC, IWDTa, and A/D self-diagnosis
• An error control module is incorporated to generate a pin signal
output, interrupt, or internal reset in response to errors originating
in the various modules.
■ Security functions (optional)*2
• Boot mode with security through encryption
■ Encoder interfaces (optional)*3
• EnDat 2.2, BiSS-C, FA-CODER, A-format, and HIPERFACE
DSL-compliant interfaces*4
• Frequency-divided output from an encoder
■ Various communications interfaces • Ethernet
- EtherCAT slave controller: 2 ports (optional) - Ethernet MAC: 1 port (an Ethernet switch is not used)or
- Ethernet MAC: 1 port (an Ethernet switch to support 2 ports is used) • USB 2.0 high-speed host/function : 1 channel • CAN (compliant with ISO11898-1): 2 channels (max.) • SCIFA with 16-byte transmission and reception FIFOs: 5 channels
• I2C bus interface: 2 channels for transfer at up to 400 kbps
• RSPIa: 4 channels
• SPIBSC: Provides a single interface for multi-I/O compatible
serial flash memory
■ External address space
• Buses for high-speed data transfer at 75 MHz (max.) • Support for up to 6 CS areas • 8-, 16-, or 32-bit bus space is selectable per area
■ Up to 33 extended-function timers
• 16-bit TPUa (12 channels), MTU3a (9 channels), GPTa (4
channels): Input capture, output compare, PWM waveform output
• 16-bit CMT (6 channels), 32-bit CMTW (2 channels)
■ Serial sound interface (1 channel)
■ ΔΣ interface
• Up to 4 ΔΣ modulators are connectable externally.
■ 12-bit A/D converters
• 12 bits × 2 units (max.)
(8 channels for unit 0; 16 channels for unit 1)
• Self diagnosis
• Detection of analog input disconnection
■ Temperature sensor for measuring temperature within the chip
■ General-purpose I/O ports
• 5-V tolerance, open drain, input pull-up
■ Multi-function pin controller
• The locations of input/output functions for peripheral modules are
selectable from among multiple pins.
■ Operating temperature range
• Tj = -40°C to +125°C
Tj: Junction temperature

伺服系统(servomechanism)又称随动系统,是用来精确地跟随或复现某个过程的反馈控制系统。伺服系统使物体的位置、方位、状态等输出被控量能够跟随输入目标(或给定值)的任意变化的自动控制系统。它的主要任务是按控制命令的要求、对功率进行放大、变换与调控等处理,使驱动装置输出的力矩、速度和位置控制非常灵活方便。在很多情况下,伺服系统专指被控制量(系统的输出量)是机械位移或位移速度、加速度的反馈控制系统,其作用是使输出的机械位移(或转角)准确地跟踪输入的位移(或转角),其结构组成和其他形式的反馈控制系统没有原则上的区别。伺服系统最初用于国防军工, 如火炮的控制, 船舰、飞机的自动驾驶,导弹发射等,后来逐渐推广到国民经济的许多部门,如自动机床、无线跟踪控制等。
伺服系统是指利用某一部件(如控制杆)的作用能使系统所处的状态到达或接近某一预定值,并能将所需状态(所需值)和实际状态加以比较,依照它们的差别(有时是这一差别的变化率)来调节控制部件的自动控制系统。
责任编辑:Davia
【免责声明】
1、本文内容、数据、图表等来源于网络引用或其他公开资料,版权归属原作者、原发表出处。若版权所有方对本文的引用持有异议,请联系拍明芯城(marketing@iczoom.com),本方将及时处理。
2、本文的引用仅供读者交流学习使用,不涉及商业目的。
3、本文内容仅代表作者观点,拍明芯城不对内容的准确性、可靠性或完整性提供明示或暗示的保证。读者阅读本文后做出的决定或行为,是基于自主意愿和独立判断做出的,请读者明确相关结果。
4、如需转载本方拥有版权的文章,请联系拍明芯城(marketing@iczoom.com)注明“转载原因”。未经允许私自转载拍明芯城将保留追究其法律责任的权利。
拍明芯城拥有对此声明的最终解释权。




 产品分类
产品分类










 2012- 2022 拍明芯城ICZOOM.com 版权所有 客服热线:400-693-8369 (9:00-18:00)
2012- 2022 拍明芯城ICZOOM.com 版权所有 客服热线:400-693-8369 (9:00-18:00)


