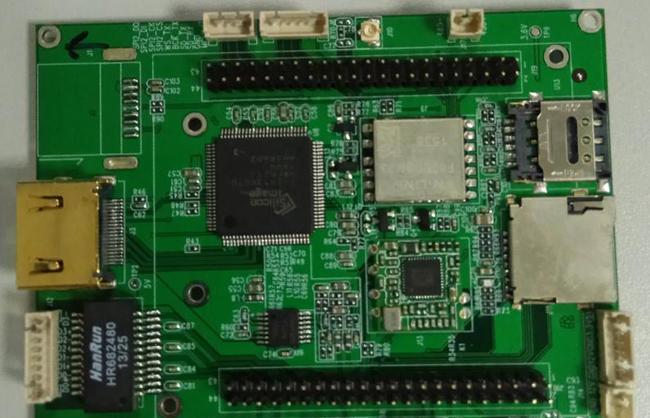
基于海思Hi3519芯片的双摄像头解决方案
 4530
4530
 拍明
拍明
应用领域:便携产品
方案类型:模块板卡
主控芯片:海思3519
方案概述
●支持有线千兆网络、兼容百兆。
●可接以下sensor类型:
IMX274:800万超低照度、OV4689:400万、IMX290:200万超低照度宽动态。
索尼、日立协议/接口的高清一体机芯。
●H.264/H.265编码可选。
●最高支持1200万sensor输入。
●支持4K分辨率(4096*2160)30帧。
●支持双路sensor输入,每路最大支持400万30帧。
●超低码率:1080P30帧2Mbits运动无马赛克
●低延时:无卡顿无拖影。
●支持双码流、支持移动侦测、支持OSD设置、支持RS485、同步模拟视频输出。
●支持TF卡128G存储、支持大容量SATA存储。
●支持TCP/IP、UDP、RTP/RTCP、RTSP、HTTP、SMTP、DNS、DDNS、DHCP、NTP等网络传输协议。
●支持SDIO WIFI和USB WIFI:热点和STA模式,
●支持4G:联通/移动/电信5模/7模
●支持双向语音对讲、支持双声道。
●支持手机APP远程观看、存储、设置。
●预留串口、数字音频I2S接口、I2C接口、SPI接口、IO口、云台控制、报警输入输出等


HISILICON HI3519 4K SOC DATASHEET
As the next-generation H.265 SoC designed for the 4K UHD IP security cameras and Sport DV cameras, the Hi3519A integrates a new-generation ISP and adopts the latest H.265 compressed video encoder, advanced low-power technology, and low-power design. This SoC is based on ARM® big.LITTLE™ architecture that combined with a powerful ARM Cortex-A17 1.2GHz core and a ARM Cortex-A7 800MHz core. The ARM big.LITTLE processing uses separate cores with different computing powers within the same CPU. The Cortex A17 core, or "big" core, handles intensive tasks like 4K UHD / 2K @30fps video encoding, and the A7 less powerful core executes less intensive tasks like intelligent video analysis.
The Hi3519A supports 90°or 270° rotation and lens distortion correction, which meets requirements in various surveillance applications. It also fully supports 3A algorithms, which allow customers to design different types of IP cameras including the IP AF zoom module. The Hi3519A integrates the POR, RTC, and audio CODEC and supports various sensor levels and clock outputs, which significantly reduces the EBOM costs for the Hi3516A HD IP camera.
KEY SPECIFICATION
Processor Core
- A7@ 800MHz,32KB I-Cache,32KB D-Cache /128KB L2 cache
- A17@ 1.2GHz,32KB I-Cache,32KB D-Cache /256KB L2 cache
- Neon acceleration, integrated FPU
- ARM big.LITTLE architecture
Video Encoding
- H.264 BP/MP/HP H.265 Main Profile
- H.265 Main Profile
- H.264/H.265 I/P/
- MJPEG/JPEG Baseline
Video Encoding Performance
A maximum of 16-megapixel resolution for H.264/H.265 encoding.
H.264/H.265 encoding of multiple streams:
4Kx2K@30fps+720P@30fps
16-Megapixel@2fps
JPEG snapshot 8-megapixel @30fps
Supporting CBR/VBR bitrate control mode,ranging: 16kbit/s~100Mbit/s
Encoding frame rate ranging from 1/16~60fps
Encoding of eight ROIs
Intelligent Video Analysis
- Integrated IVE, supporting various intelligent analysis applications such as motion detection, boundary security and video diagnosis
- 3D denoising, image enhancement, and dynamic contrast enhancement
- Anti-flicker for output videos and graphics, 1/15.99x to 16x video scaling
- 1/2x to 2x graphics scaling
- OSD overlay pre-processing for eight regions
- Video graphics overlaying of two layers (video layer and graphics layer)
ISP
- Adjustable 3A functions (AE, AWB, and AF)
- Noise reduction in FPN mode
- Highlight compensation, backlight compensation, gamma correction, and color enhancement
- Defect pixel correction, denoising, and digital image stabilizer
- Defog
- Lens distortion correction
- Picture rotation by 90° or 270°
- Mirroring and flipping
- Digital WDR, 4F/3F/2F - Frame base/Line base WDR, Tone mapping
- ISP tuning tools for the PC
Audio Encoding/Decoding
- Voice encoding/decoding in compliance with multiple protocols by using software
- G.711, ADPCM, and G.726 protocols
- AEC, ANR, and ALC
Security Engine
- Various encryption and decryption algorithms using hardware, such as AES, DES, and 3DES
- RSA1024/2048/4096 Signature verification algorithm
- Hardware Tamper-resistant HASH algorithm, support HASH SHA1 / 256, HMAC SHA1 / 256 Algorithm
- Integrated 512Bit OTP storage space and hardware random number generator
Video Interfaces
- Input
− 8-/10-/12-/14-bit RGB Bayer DC timing VI, a maximum of 150 MHz clock frequency
− BT.601, BT.656 or BT.1120 VI interface
− 12xLane MIPI/LVDS/Sub-LVDS/HiSPi
− Compatible with mainstream HD CMOS sensors provided by SONY, ON Semiconductor, OmniVision, Panasonic
− Compatibility with the electrical specifications of parallel and differential interfaces of various sensors
− Programmable sensor clock output
- Output
− One PAL/NTSC output for automatic load detection
− One BT.1120/BT.656 VO interface for connecting to an external HDMI or SDI, up to 1080p@60 fps output, support LCD output
Audio Interfaces
- Integrated audio CODEC, supporting 16-bit audio inputs and outputs
- I2S interface for connecting to an external audio CODEC
- Stereo Mic differential input, reducing background noise
Peripheral Interfaces
- POR
- One integrated high-precision RTC
- One quad-channel SAR ADC
- Five UART interfaces
- IR Interface, I2C Interfaces, SSP master interfaces, GPIO Interfaces
- Eight PWM interfaces (four independent interfaces and four multiplexed with other pins)
- Two SDIO 3.0/SDIO3.0 interfaces, supporting SDXC
- One USB 3.0/2.0 host/device port
- One PCIe2.0 master/slave mode
- RGMII/RMII/MII in 100/1000 Mbit/s full-duplex or half-duplex mode, PHY clock output, and TSO network acceleration
External Memory Interfaces
- DDR3/3L SDRAM interface
− One 32-bit DDR4/3/3L interface with the maximum frequency of 800 MHz (1.6 Gbit/s)
− Maximum capacity of 1024MB for a 16-bit DDR
− Maximum capacity of 2048MB for two 16-bit DDRs
- SPI NOR flash interface
− 1-, 2-, or 4-wire mode
− Support 3Byte, 4Byte address mode
− Maximum capacity of 32 MB
- SPI NAND flash interface
− Maximum capacity of 512MB
- eMMC5.0 interface
− maximum support 64GByte z NAND Flash interface
− 8bit data width
− SLC, MLC − 4, 8, 24, 40, 64bit ECC
− 8GBabove devices
- Booting from the SPI NOR flash, SPI Nand Flash or NAND flash
- Booting from eMMC
SDK
- Linux-3.4-based SDK
- High-performance H.264/H.265 PC decoding library
Physical Specifications
- Power consumption
− 1.5W typical power consumption @4K*2K
− Multi-level power-saving mode
- Operating voltages
− 0.9V core voltage
− 3.3 V I/O voltage and 3.8 V margin voltage
− DDR4/3/3L SDRAM interface voltage 1.2/1.5/1.35 V
- Package
− RoHS,TFBGA
− Body size of 15 mm x 15 mm
− 0.65mm (0.03 in.) ball pitch
【相关信息】双摄像头系列原理深度剖析
摄像头的应用主要分为:距离相关的应用,光学变焦,暗光补偿以及3D拍摄和建模。每种应用的原理都有些不同,我们就分别介绍一下相关的原理:
距离相关应用
人眼是很容易对一个物体的距离进行定位,但当人闭上其中一个眼睛后,定位能力就会下降很多。
双摄像头就是模拟人眼的应用。
简单的说,测距离的话,就是通过算法算出,被拍摄物体与左/右摄像头的角度θ1和θ2,再加上固定的y值(即两个摄像头的中心距),就非常容易算出z值(即物体到Camera的距离)
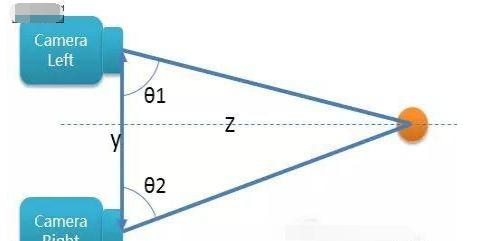
不过这也很容易推算,若两个摄像头中心距过小的话,可计算的物体距离就会很近。若想算出很远距离,就必须让左右摄像头的距离拉远。
光学变焦
光学变焦主要是左右摄像头使用不同的FOV(可视角),这样两个摄像头取景不同。当用户需要广角照片,则用视角为85度的左摄像头取景,获得广角效果。当用户需要长焦照片,则用视角为45度的右摄像头取景,获得长焦效果。
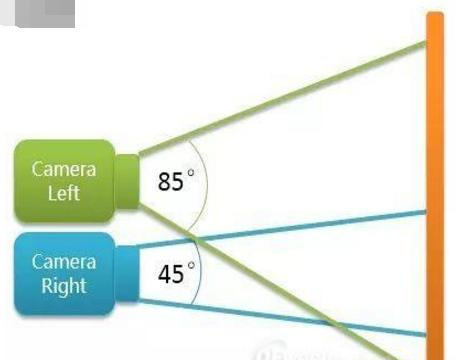
为了使左右摄像头拍摄的物体重叠度高,光学变焦的双摄像头模组不能像做距离应用的摄像头的模组那样距离过大,而是需要将左右摄像头摆得越近越好。
暗光增强
其实第二篇的时候,小编已经简单介绍过暗光增强的原理。一般来讲,做暗光增强就是将两个摄像头一个用RGBG的标准摄像头,一个用去掉RGBG 滤波片的黑白摄像头。RGBG用来获得物体的色彩,而黑白摄像头用来获得更好的进光量,来判断被拍物体的光强强度。然后将两个图片融合即可获得更好的暗光增强。
只是一般来说,有两种融合方法:
1. 以黑白图片为主体,将彩色图片上获取的每个像素的颜色贴至黑白图片上,将两种图片融合。
2. 以彩色图片为主体,将黑白图片上获取的每个图像的光亮强度补偿到彩色照片上,将两种图片融合。
至于哪种方式更合适做融合,可能仁者见仁智者见智,就不在这展开讨论了。
同样,做暗光增强,为了让左右摄像头拍摄的物体重叠图高,此类双摄像头模组也是要求越近越好。
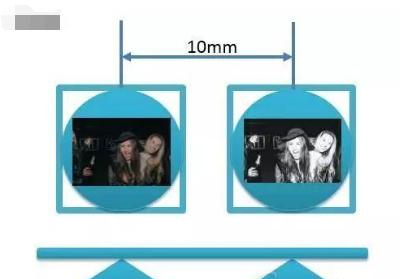
需要说明的事,华为P9 其实选用的就是这个方式的模组。
当然有些业内人士也表示这种算法目前做的效果并不明显。暗光补偿对用户来的确很帮助,尤其拍夜景的时候。不过有些客户认为索尼和三星的Dual PD技术就非常好,更愿意用Dual PD 摄像头来做暗光补偿。
到底是双摄像头还是Dual PD的暗光补偿效果好,大家可以比较一下华为P9和三星的Galaxy S7 edge,就会有答案了。
3D拍摄和3D建模
3D拍摄和3D建模的算法其实跟距离应用有点类似,只是它的精度要求更高,甚至有时会需要用红外测距进行更准确的距离判断。在这里小编就不详细展开介绍了。
对ISP的要求
提到双摄像头的算法,不得不提到ISP(Image Signal Processing 图像信号处理器),ISP主要作用是对前端图像传感器输出的信号做后期处理,主要功能有线性纠正、噪声去除、坏点去除、内插、白平衡、自动曝光控制等,依赖于ISP才能在不同的光学条件下都能较好的还原现场细节,ISP技术在很大程度上决定了手机的成像质量。
功能机时代,ISP都是做在摄像头上的,不同像素的摄像头搭配不同性能的ISP。随着手机摄像头像素越来越高,对ISP性能的要求越来越高,若将ISP集成到摄像头Sensor上,势必造成摄像头的模组过大,甚至影响拍照效果。所以智能机时代,ISP一般都是在主芯片SoC上。部分品牌客户为了实现更好的效果,甚至不惜成本的外加一颗ISP用来达到更好更专业的拍照效果。
好的拍照算法就需要搭配好的ISP,ISP和算法相辅相成,缺一不可。而双摄像头对ISP性能要求更多。首先,为了使的左右摄像头的信号能够同时被处理,单一的ISP已经无法满足双摄像头的需求。这就需要双路ISP实现此功能。
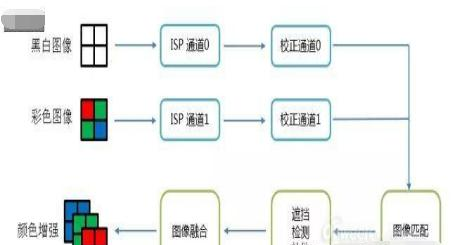
以暗光增强为例,彩色/黑白图像分别进入各自的ISP通道和校准通道,然后将两副图片做匹配(如将两幅图片相同的部分提取出来,去除只有一个摄像头拍到的部分),然后通过遮挡,检测,补偿等算法 处理相关的图片。最后将两幅图片融合起来,实现颜色的增强。当然实际上ISP配合算法做的事情,远远比这图片上写的要多。小编实在不知道,就不在这误导大家了。
当然,在这里面也有一个小小的插曲。毕竟是两个ISP,两个ISP多少有一些处理速度,处理能力不同的问题。为了保证两个ISP能在同一时间上取样,就需要双摄像头拍出来的图片是同一时间拍出来的。其中一个解决办法就是让Sensor有一个同步信号引脚。将两个摄像头的同步信号对接,在每次读取图片时,将图片都打上一个时间戳,ISP通过时间戳,保证左右摄像头拍出来的照片在同一时间拍摄,最终再进行融合。
摄像头的接口
一般来讲,目前的智能手机的摄像头接口都是MIPI接口。之前手机平台都只有2路MIPI接口,分别给前摄像头和后摄像头。做双摄像头,就要求平台至少支持三路MIPI接口。其实在之前的高端平台上,为了实现更高像素,已经用双路ISP了(比如为了支持16M的摄像头,会用2路8M能力的ISP),这类平台很有可能只有两路MIPI。但这个无法阻止工程师去做前单摄像头+后双摄像头。
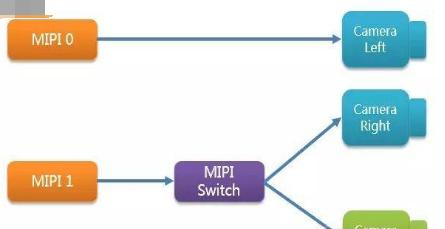
没错,加一个小小的Swtich,就可以轻松实现双摄像头。
责任编辑:Davia
【免责声明】
1、本文内容、数据、图表等来源于网络引用或其他公开资料,版权归属原作者、原发表出处。若版权所有方对本文的引用持有异议,请联系拍明芯城(marketing@iczoom.com),本方将及时处理。
2、本文的引用仅供读者交流学习使用,不涉及商业目的。
3、本文内容仅代表作者观点,拍明芯城不对内容的准确性、可靠性或完整性提供明示或暗示的保证。读者阅读本文后做出的决定或行为,是基于自主意愿和独立判断做出的,请读者明确相关结果。
4、如需转载本方拥有版权的文章,请联系拍明芯城(marketing@iczoom.com)注明“转载原因”。未经允许私自转载拍明芯城将保留追究其法律责任的权利。
拍明芯城拥有对此声明的最终解释权。




 产品分类
产品分类










 2012- 2022 拍明芯城ICZOOM.com 版权所有 客服热线:400-693-8369 (9:00-18:00)
2012- 2022 拍明芯城ICZOOM.com 版权所有 客服热线:400-693-8369 (9:00-18:00)


